EXPERTISE OF HOUSE & BUILDING FOUNDATION CRACKS
THE EXPERTISE OF CRACKS REVEALS 3 TYPES OF GENERIC CRACKS
I – Structural cracks:
Cracks are the result of the link between your building and the soil which must be considered as a whole “construction”.
Your house (single storey) must restore its mechanical load to the soil, which can be averaged at 2.5 to 3.2 T / m2. So your foundations, the footings for a 100m2 house will transmit 300 tonnes to the soil, which is quite significant.
It should be understood that the mechanical resistance of the soil and its contact surface will limit, depending on its dimensioning, the repercussions of soil movements and therefore of structural cracks, or foundation cracks. In this case, for the standard 25m2 seat soles, a load of 12 T / m2 will be transmitted to the soil.
Of course the compression bulb (zone of influence) will have its impact, the nature of the soil will be important in the process and will impact the foundation cracks.
This being said, the mechanical structure of your sub-works (foundations as a whole) will have its importance: types of steels entering the foundation reinforcement cage, the choice of constructing a collaborating raft foundation etc.
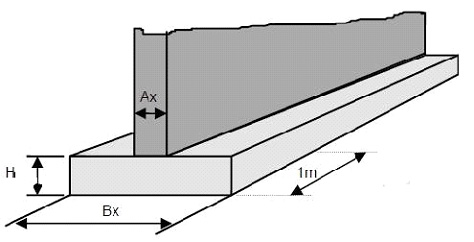
Footings of the house
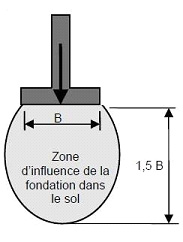
Subwork impact / soil
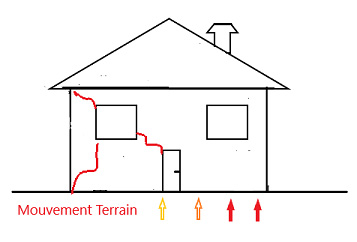
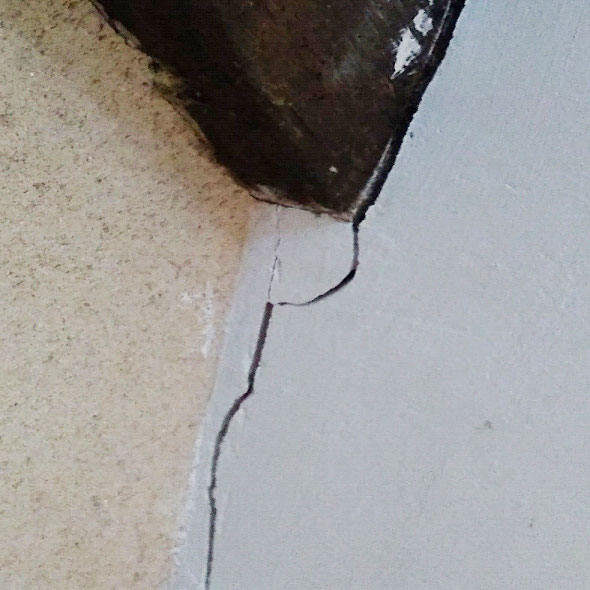
Structural cracks ; staircase
II – External appearance of mechanical cracks:
These so-called “wall cracks” are the result of the use of materials in conjunction with poorly prepared or prepared substrates disregarding the prescriptions of the supplier of incoming products.
We find these cracks in:
- The implementation of plasters,
- The installation of external thermal insulation composite system (ETICS)
- Painting over existing old paint.
These poor implementations lead to initially minor cracks on the wall considered to be insignificant.
Yet, the consequences of these cracks on the wall over time can endanger the coating and therefore the protection of the building.
Choice of mutually incompatible materials revealed during the crack expertise

Cracks on wall and façade degradation
In red: the refreshment made 5 years ago created a waterproof barrier preventing the façade from breathing: creation of blisters before fall.
In blue: the crack allowed the penetration of water which has “eaten away” the lintel (upper part) of the window: important work to be planned.
III – Interior aspect of mechanical crack:
These cracks can be either:
- the restitution of structural cracks already observed on the outside of the building: seeing them in symmetry to those on the outside is a high severity indicator.
- the result of the use of two materials which have different behavior and mechanical reaction.
Example: you install partition walls or ceilings or dividers in plasterboard (BA 13) in conjunction with beams, wooden board, you will therefore see aesthetic cracks on the wall or even crevices.
The plasterboard being very rigid compared to the wood, it will not be able to follow the movement of this one (the expansion of the wood versus the expansion of the BA 13).
In this example, the consequence is that one or more wall cracks will appear at the level of the link between these two materials.
As these are non-structural cracks, we will call them aesthetic cracks, they will not be taken care of, in particular by insurers. Indeed this arises out of faulty advice or implementation. But there are smart solutions to resolve the consequences of these cracks.

